Payment for extra work
Building works are complex, and it is common for a contractor to carry out works not described in the original contract documents for which they consider they are entitled to additional payment over and above the original contract sum. However, the fact that a contractor has carried out extra work does not automatically mean they have a right to payment for it.
The exact conditions under which additional payment is merited should be set out in the terms of the contract, however, generally, the contractor must be able to prove the following:
- The contract sum does not include the additional work.
- There was an express or implied promise to compensate the contractor for the work.
- The work was instructed by an authorised agent.
- Any conditions precedent to payment, as imposed by the contract, have been fulfilled.
For example, where the contractor has carried out extra work or uses superior materials to those specified, but they have not been instructed to do so, this will not entitle them to extra payment. Similarly, if the employer agrees to different work, they will not necessarily be liable for any additional payment if they were not informed of the increased costs involved.
Generally, in an emergency situation where a contractor pays a sum to preserve the employer’s property, and has not been possible to obtain instructions from the employer, the contractor will be entitled to additional payment.
If the employer refuses to provide additional payment for extra work, the contractor may refuse to carry out the work. If the employer promises the additional payment, and it later transpires that the work is included in the original contract sum and so is not ‘extra’, the promise to pay will generally not be binding.
Even if the employer has had the benefit of extra work, in the absence of written instructions, it is generally held that the contractor will be unable to recover payment.
The contractor should consider whether what they think is ‘extra work’ is provided for by the clauses of the contract.
Typically, contracts provide for changes to the works described in the contract documents through variation clauses. A variation (sometimes referred to as a variation instruction, variation order or change order) is an alteration to the scope of works in the form of an addition, substitution or omission from the original scope of works. Variations may also be deemed to occur if the contract documents do not properly describe the works actually required.
Variation instructions must be clear as to what is and is not included, and may propose the method of valuation.
For more information see: Variations.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
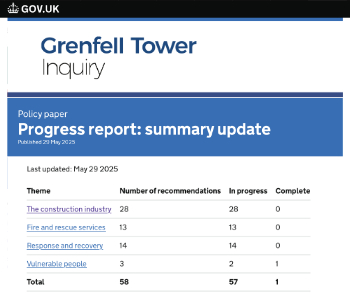
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.